The acronym PTE stands for Potentially Toxic Elements and is commonly used in Science to define a group of elements, which can be found naturally in soils, water and sediments we have to be aware of. These elements are arsenic (As), cadmiun (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), fluoride (F), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn). PTE toxicity doesn’t depend on their presence itself but on their concentration.
Concentrations matter!
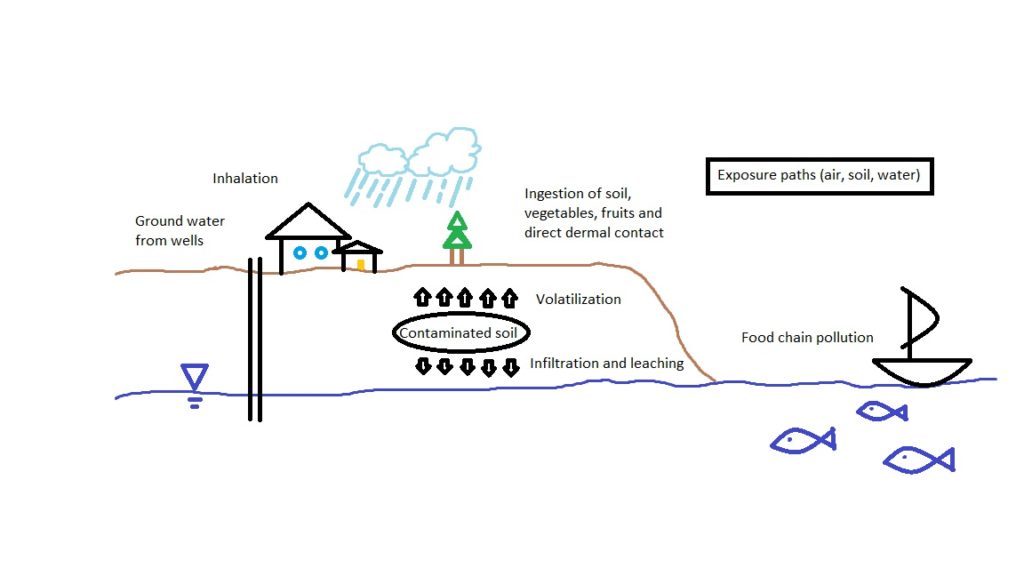
The potential toxicity is due to the possibility of those elements to accumulate over time and above certain limits to be harmful to humans, animals and in general to the environment. This increment can be due to urbanization, agricultural activities, industry or mining, which in certain situations may help a creation of a heavy metals reservoir. Those elements can be dangerous because they can enter through food, water and air in our bodies. It is also true that they are naturally present and essential for life, but at high concentrations they are toxic.





zortilo nrel
27 Nov 2021Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…